Worried that your child may have sensory processing challenges? Here are some patterns of behaviors to look out for that can be indicative of sensory processing differences.
Sensory Processing Red Flags
- Over-responsive to sensory input:
- Expresses discomfort in response to loud sounds or bright lights
- Aversive to light touch, teeth brushing, hair grooming, or clothing textures
- Hesitant to climb and use moving playground equipment (swings, bikes)
- Gags in response to certain smells or food textures
- Under-responsive to sensory input:
- Constantly “on the move”
- Does not appear to register sensory stimuli, such as being touched or bumped
- Craves frequent or intense sensory experiences (climbing, jumping, crashing)
- Motor Skill Challenges
- Appears clumsy
- A limited repertoire of play activities
- Difficulty letting peers “take the lead” in play
- Avoids novel play activities or environments
- Self-Regulation Challenges
- Easily distracted by visual stimuli or background sounds
- Becomes overwhelmed, has meltdowns, or avoids multi-sensory environments, such as birthday parties, public events, or the classroom
- Has difficulty transitioning between environments or activities
My child shows some sensory processing challenges, what is next?
Just like people have individual personalities, we all have unique sensory preferences. As an adult, you have likely learned to cope with sensory and life stressors by seeking out input (either consciously or subconsciously) that is regulating for your sensory system. For example, you may take a warm shower to relax your body after a long day, go for a run to feel organized, or listen to music on headphones at a busy store. These sensory strategies help “feed” the nervous system and allow you to maintain a functional, regulated state.
Kids need support and guidance to find the inputs that help them feel “just right.” Here are some strategies that are generally calming for the nervous system. As always, these are child-led activities. Monitor your child’s response; if they have an aversive response or just do not like the activity, stop immediately.
Proprioceptive Input (input that engages the muscles and joints):

- Pushing a shopping cart, carrying a backpack with heavy library books, or climbing on playground equipment
Deep touch pressure to the whole body:

- Massage, weighted blankets, or big hugs!
Rhythmic linear movement:
- Rocking on a rocking chair, rocking slowly on a supportive swing, or jumping on a small trampoline

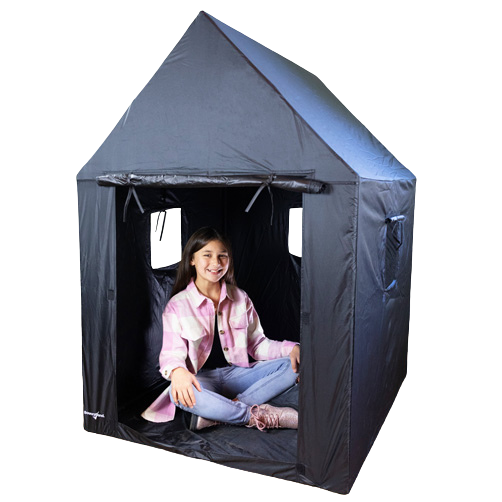
Cozy fort-like spaces:
- Create cozy fort-like spaces with a pop-up tent or blanket and chairs. Be sure to include favorite stuffed animals, books to look at, and fidgets to squish.
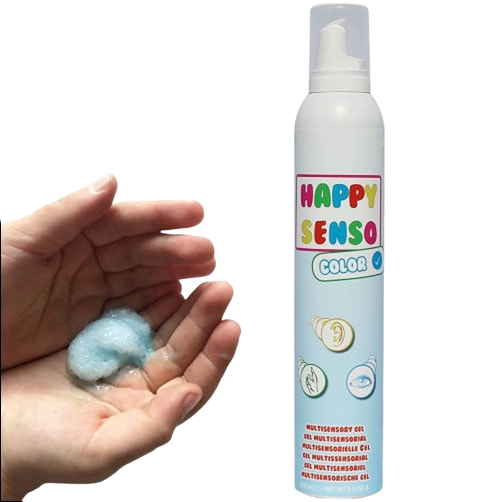


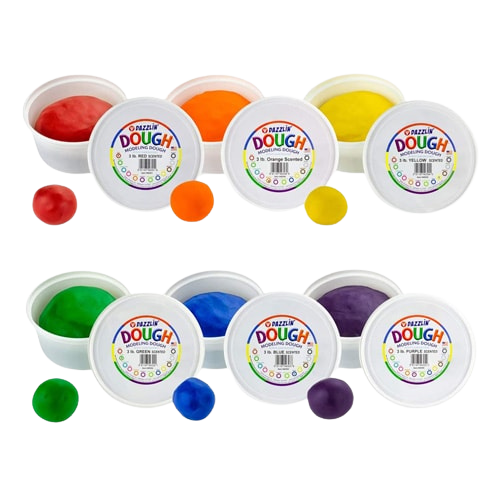
- Explore different tactile bin play such as dry rice, putty, Kinetic Sand, or foam soap. Note: kids who are tactile sensitive may be aversive to this type of play so always invite into play but never force interaction.
- Pro tip: If a texture is new, you can put it in a plastic baggie, allowing the child to interact without sticky hands!
Olfactory support:
- For children who are hypersensitive to smell: Limit the use of scented sprays, soaps, cleaning products, or candles, and allow fresh air to circulate in your home.
- For children who are not hypersensitive to smell: fresh flowers or satchels can be useful in creating a calming environment. Lavender and chamomile are known for their calming properties. Note: Exercise caution when using aromatherapy as children tend to be more sensitive to smell than adults.

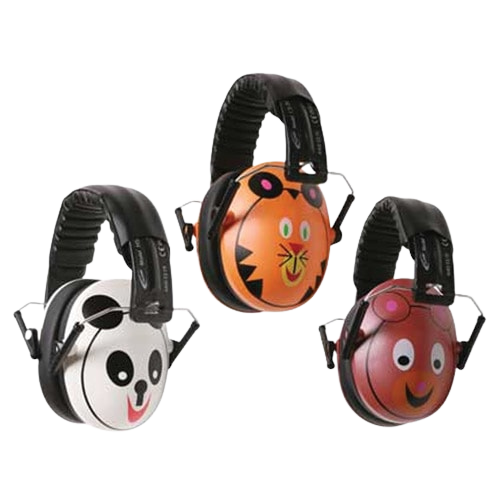
Over-responsivity supports:
- Use noise-cancelling headphones to block out distracting or bothersome background noise
- Wear a hood, hat, or sunglasses to help mute bright lights or visually busy environments
- Providing a quiet space with dim lighting to take breaks from a chaotic environment

Need more help?
If you need more guidance, reach out to your local pediatric occupational therapist who specializes in sensory processing and sensory integration therapy. You may benefit from additional parent support or your child may benefit from occupational therapy treatment.
Guest Blogger: Taylor Mason, OT
Taylor Mason has 13 years of experience as an occupational therapist and is the proud owner of The Nurture Nook, a company dedicated to providing virtual support for parents of children with sensory and developmental challenges.