On June 8th the Therapro team was supposed to set up a booth at the 2023 New York City’s Department of Education (NYCDOE) Assistive Technology Expo but unfortunately poor air quality from the Canadian wildfires meant the event was canceled. However, we still wanted to showcase the many ways assistive technology can be used, in the classroom, to engage all learners. In this blog post we are covering the modification ideas we were planning to display at the conference.
Reading
There is a lot involved in reading a book; readers must have the ability to attend and focus, they must have the fine motor ability to turn the pages of a book, and they must have the visual skills needed to see the words on the page. When reading a book is further complicated by these challenges, engagement can decrease. Fortunately, there are several ways assistive technology can be used to address these challenges.

Adaptations for Low Vision or Decreased Focus
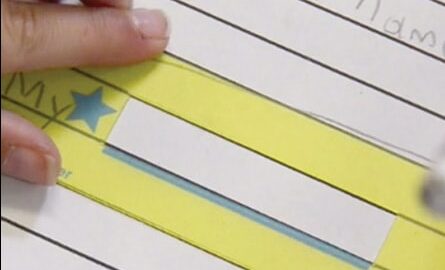
Highlighter strips are simply strips of specially designed yellow material that stick to the pages of a book with static electricity. Highlighter strips brighten written words on a page making visual processing easier. These strips are especially useful for students with attention difficulties or who have low vision.
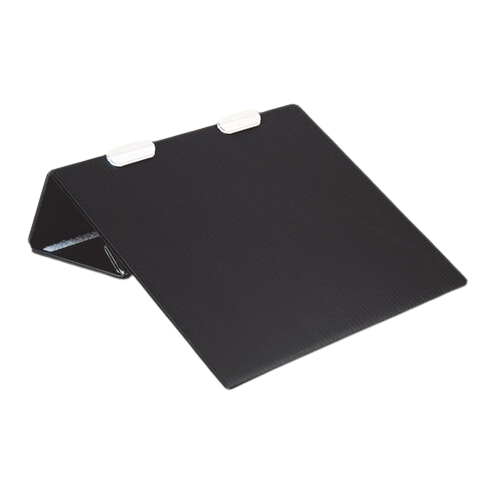

Slant boards have a variety of uses, for students who have difficulty with attention and focus they are a great tool to use when reading! The angle of the board will bring the book closer to eye level minimizing distractions and increasing focus. Pro tip: Learn more about the different uses of slant boards in our previous post: More Than Just A Slant Board!

Adaptations for Fine Motor Difficulties
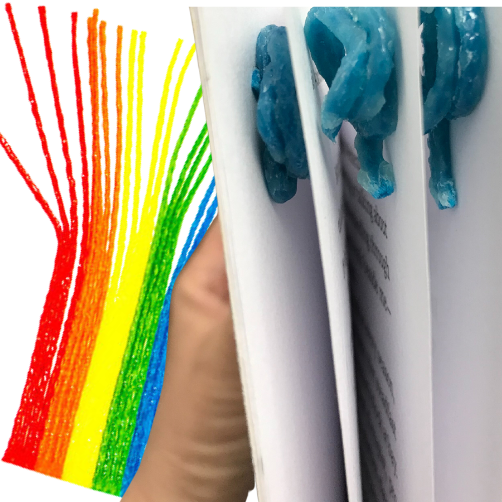
Wikki Stix are wax colored strings that are often used for craft projects. However, these moldable, slightly sticky strings are a great option for creating removable ‘page lifts’. Simply shape the Wikki Stix into a small spiral or mound and place one on each page of a book. This will separate the pages of the book making it easier for students with fine motor limitations to turn the pages of the book.

Adaptations for Emerging Readers
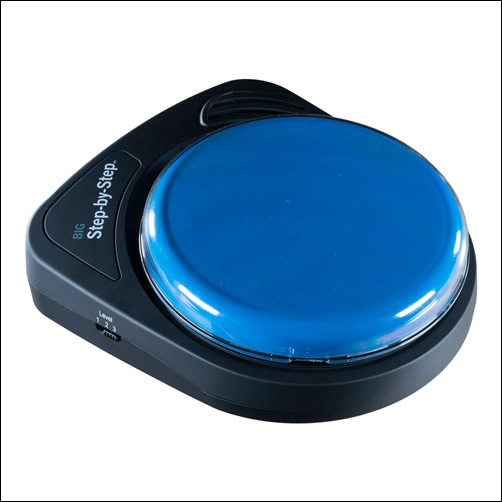
Step by Steps (available as Little or Big) are often used as communication devices. However, they can be a handy tool for learners with limited or emerging literacy skills. To use, record as you read aloud the pages of the book. When the user is ready to ‘read’, they would hit the switch to hear the recording of the book. To make this more interactive and to better imitate the act of flipping through the pages of a book, use the sequential feature to record page by page. With this the ‘reader’ would hit the switch to hear what is on the next ‘page’.
To learn more about supporting literacy skills check out the January 2022 post, Supporting Reading: More Than Just Literacy Skills
Writing
Just like reading a book, writing also requires many skills; these skills include the fine motor ability to effectively hold a writing utensil, the visual perceptual ability to coordinate visual input with motor output, and the sensory ability to accurately grade force. Difficulties in any of these areas can adversely effect handwriting legibility, speed, and endurance for writing tasks. The good news is that there are many accommodations and modifications that could be used to help with these difficulties.
Adaptations for Decreased Handwriting Legibility
Handwriting legibility is often influenced by writing with poor sizing, difficulty orienting letters to the writing line, or letter spacing issues. Check out some of the options available to address these areas.
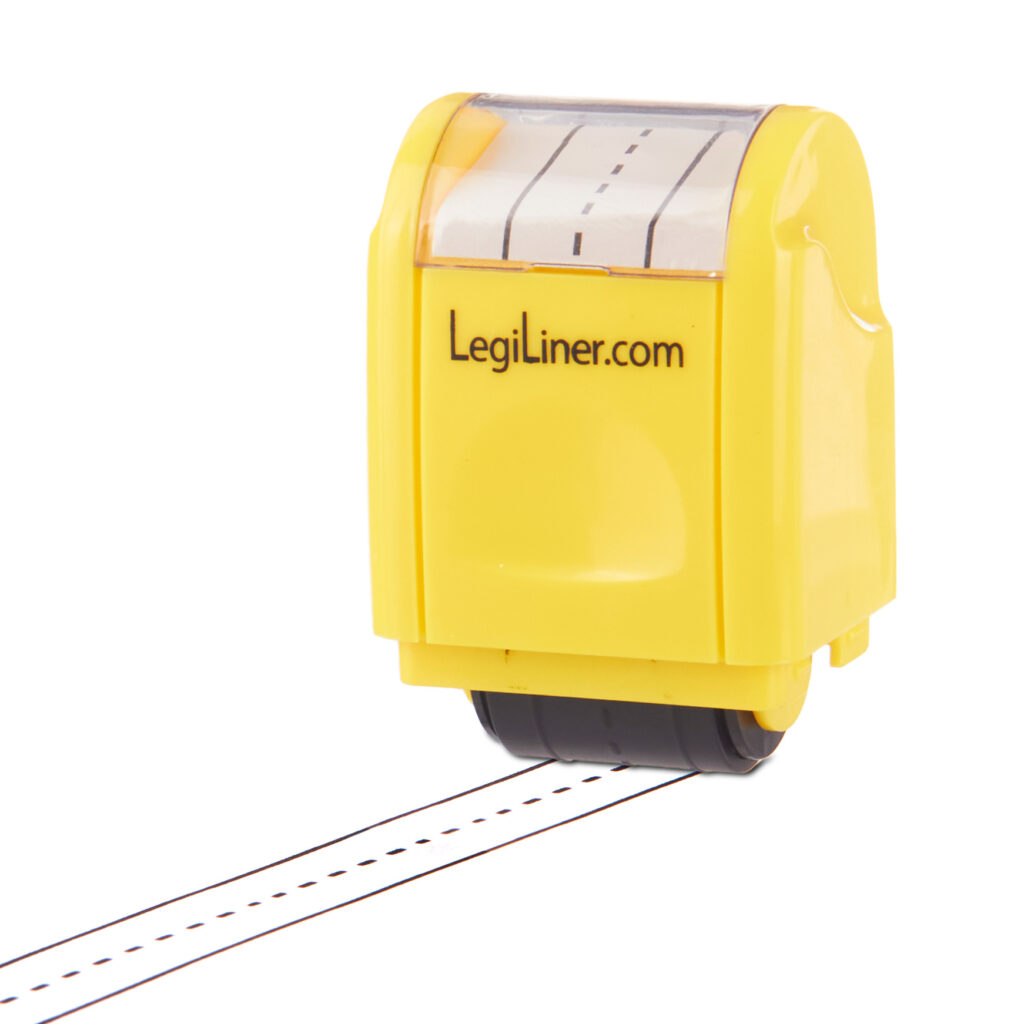
- LegiLiners: LegiLiners are a rolling ink stamp that can be used to create a writing line on paper with open spaces. A writing line can be a game changer for students who have difficulty writing with the appropriate size. LegiLiners are available in a variety of styles and even have some great options to help out in math class!

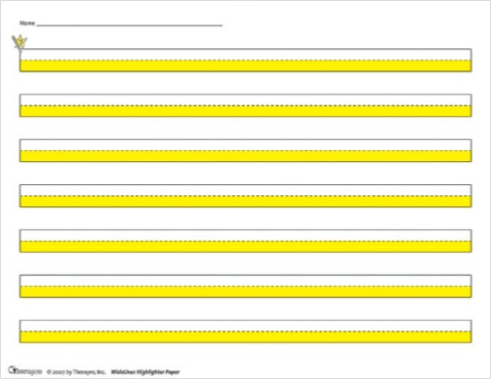
- Highlighter Paper: Highlighter paper features highlighting in the lower writing area (available is yellow or blue). This highlighting helps indicate where letters should be placed. Another feature of highlighter paper is that the solid lines have been separated to assist the student with locating the writing area.
- Raised Line Paper: Raised line paper is a unique paper that features a subtle raised line to indicate the top and bottom writing line. These gentle cues can be a great reminder for students who write outside of the writing area.

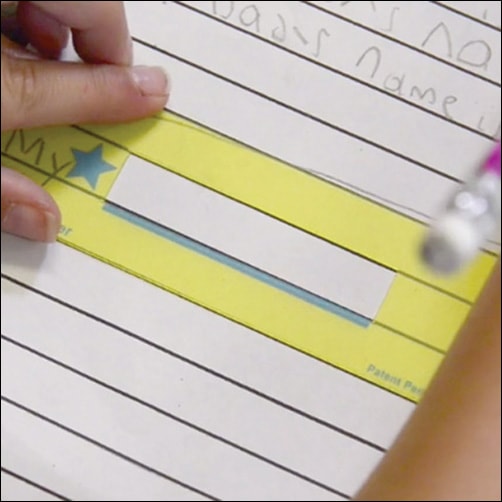
- Spacers: Finger Spacers and Star Spacers each offer support to help students better understand correct spacing. The Finger Spacer is a great tool to teach correct spacing between written words; it is available as a one finger (1st to 3rd Grade) or two finger Pre-K to 2nd Grade) spacer. The Star Spacer is a clever handwriting tool made of see-through plastic that acts as a guide to help the child understand spacing, sizing, and alignment of letters and words to promote more legible handwriting.
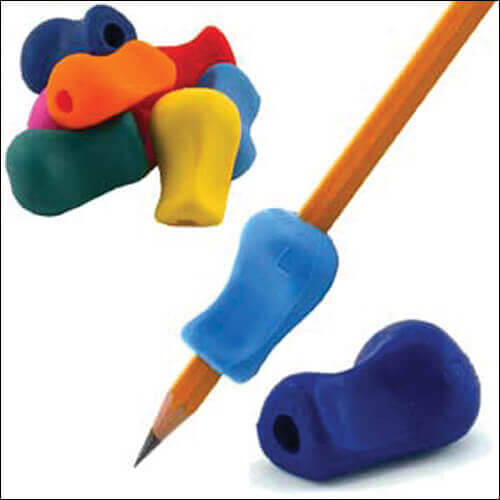


Handwriting Speed & Endurance
Handwriting speed and endurance for writing tasks is often impacted by difficulties related to grasp. Pen and pencil grips are a quick and easy solution. The blog post Get A Grip on Pencil Grips and Adapted Writing Tools! covered this topic extensively. Therapro also has a free handy guide, Get A Grip on Pencil Grips that helps determine the best grip to fit your needs.
Extracurricular Activities
Difficulty grasping objects can impact a student’s ability to not only participate in academic tasks but can also impact the student’s ability to participate in extracurriculars like music or art class. Two unique devices to help with grasp and grip are the Eazyhold Universal Cuffs and the the functionalhand.
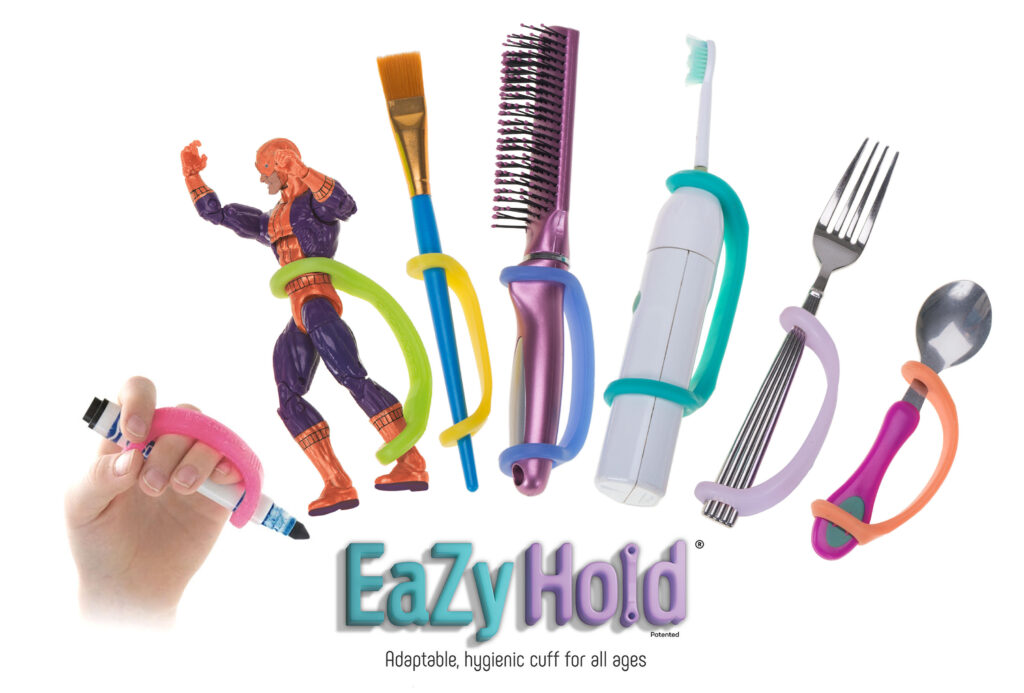

Eazyhold Universal Cuffs are an innovative solution to help students who have a weak or non existent grasp. These handy tools can be used not only in the classroom but also during extracurricular activities like holding a paintbrush in art class, holding drumsticks in music class, or a water bottle during gym. The silicone strap simply drapes over the back of the hand and the object is inserted into the two holes on opposite ends of the Eazyhold allowing the object to be securely held with the palmer side of the hand. Pro tip, not sure which Eazyhold is right for you? Check out Therapro’s What Can I Adapt Handy Guide for sizing recommendations!
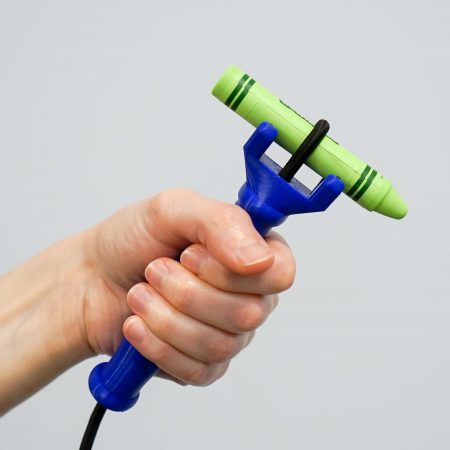

The functionalhand is another tool to aid grasp. The functionalhand‘s unique and flexible design allows the users to hold functional tools of many shapes and sizes in both the vertical and horizontal orientation. It is truly a universal cuff that is durable and supports a wide age range and types of disabilities. Pro Tip the functionalhand and Eazyholds work great when paired together to offer students both control and a secure grasp on tools.
Therapro had many ideas ready to display at the 2023 NYCDOE Assistive Technology Expo; we are disappointed we couldn’t meet you all in person but we are glad to have the opportunity to share these ideas here!