Linda Merry, OTR/L, NDT/C
What is Executive Function?
The phrase “executive function” as described in the Harvard Journal, Developing Child, refers to a set of skills. These skills underlie the capacity to plan ahead and meet goals, display self-control, follow multiple-step directions even when interrupted and stay focused despite distractions, among others.
No one is born with executive function skills but nearly everyone can learn them. Adults set up the framework for children to learn and practice these skills over time by establishing routines, breaking big tasks into smaller chunks, and encouraging activities involving rules, directions and planning skills.
As our child becomes more competent and these areas of the brain develop, it enables them to plan for themselves. It also allows them to focus and stay engaged with information to complete tasks. Research has shown by 12 months of age, a child’s experiences are helping to lay the foundation for the ongoing development of executive function skills.
Get Ready, Do, Done
Sara Ward and Kristen Jacobsen’s framework, “get ready, do, done”, to support skill development provides a process to develop the executive functioning abilities. This system is easily incorporated into all activities.
Implementation
The first step is to help your child or student visualize what the project will look like when it is done i.e., what does the end look like. Children need the opportunity to visualize the end before they plan their steps. This is especially true for a child who lacks the motor control to move their body or communication skills to verbalize their intent. A child may have the ability to plan a task but lack the opportunity when others bring materials to them, place them on their surface and physically help with each step.
Next, you want the child to visualize the steps they need to take. It may involve cutting a circle, drawing a picture, gluing, etc. You want your child to think through the process. Let the child tell you what steps they want to take before beginning.
Last, to “get ready” the child should tell you what materials they need. Is it markers, paper, ruler, glue stick, etc.?
Accessibility For The Child With Special Needs.
When a child can visualize what their completed project looks like, they can talk through the process and collect needed materials as independent as possible. What if a child is unable to communicate verbally or walk over to get what they need? Here are strategies that provide inclusive opportunities to use this framework. It allows the child with neuromotor difficulties to participate in opportunities that lay the foundation for executive functioning. The goal is to support their abilities and not allow their impairments to limit their learning.
Get Ready, Do, Done provides a visual or template to clearly demonstrate the thinking process.
Strategies To Support Inclusive Learning
- Positioning Needs of the Child: When completing activities that require attention, concentration and upper extremity control, optimal positioning is important. A child seated upright so they can view what their project looks like when completed. Positioning the child at 90:90:90 for the hips:knees:ankles with feet supported is usually preferred.
- Tray Surface: Supporting the upper arm on a table surface provides a base of support for upper extremity control. By increasing the contact surface of the forearm and hand, it provides stability and increased sensory awareness of movement in space. We have found a tray surface that supports the elbows, by curving around the body, makes a significant difference. The work surface should be large enough to fit materials and support the upper body. Common errors are elbows falling off the table or not enough room for materials.
- Organization of Work Surface: For the individual with motor coordination, it can be helpful to have a container where materials are placed avoiding knocking them off the tray. This can be a small bowl or box that serves as a “waiting area” for items such as scissors and glue.
- Vision Considerations: The size, colors and position of the project are important. Placing the project that is “done” and showing what the end looks like should be of a size, position and contrast that supports vision needs. Placing it on an easel, on the wall or at an angle that allows for easy viewing is helpful and allows the child to visually reference the project that they are completing. Adjusting the size by enlarging pictures or having a black contrasting background may help the individual with vision impairments.
- Activity Selection/Material Considerations: Using templates and/or pre-made cut outs may help the individual with motor impairments. If the end is a picture of a farm, using a template that supports coloring inside can be helpful. Using stickers that allow the individual to place or glue them reduces the motor demands. Forming Wikki Stix into shapes that allow the child to color inside simple shapes is another option.
- Tool Use: Using adaptive crayons or adapted markers, glue sticks and other materials may allow the child to do the task without hand over hand assistance. You want to reduce the motor demands when you increase the cognitive requirements. There are many options to help children hold their own tools. The Functionalhand allows children to hold objects in either the horizontal or vertical orientation. Any size crayon, marker, glue stick, dry erase markers or school tools can fit into the flexible cord system. For children who are unable to sustain a grasp on the Functionalhand independently, the Eazyhold strap is the ideal complimentary product.

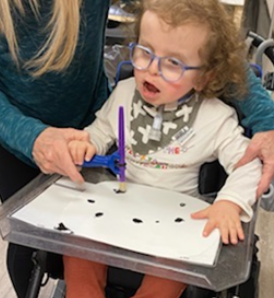
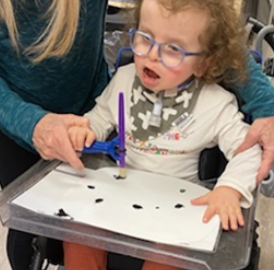
Do
Keeping the activity initially simple and building on the concept once the child is familiar is important. Initial activities may be to color pictures and glue them in position. Having two sets of icons, one showing the action and the other showing the tool helps them to understand the difference.


You may start by showing the pictures and asking, “do we cut first or color first”. Using “first” and “then” concepts allows your child to know there is a progression to activities and reflect on the order. The child can point, answer or place the icons in order.
Get Ready
Several strategies will assist the individual to be actively engaged in the “ Do” and “Get Ready” process.
- Use picture icons that allow the child to point to or grasp to put in the “Get Ready” column. Using Velcro to keep the pictures in position may be helpful.
- Use an augmentative communication device with a page that lists options and allowing the child to point to or use a stylus to access their selections individually. The child can then grasp the item to put into their “waiting area” bowl or box or you place them upon making their selection.
Summary
How does a child with neuromotor impairment that may lack the postural control to move, reach and communicate get the same opportunities to develop executive functioning skills as other children? Structuring the learning opportunity and providing activities in a manner that supports their thought processes to plan and participate in the execution of tasks is important. Incorporating alternative strategies to minimize hand over hand assistance is the start. The key is to let the child do as much for themselves as possible both in terms of thought process and motor participation. Learn more about Executive Functioning by listening to Therapro’s Lecture series on this and other topics.
References
Ward, S., & Jacobsen, K. (2014). A clinical model for developing executive function skills. Perspectives on Language Learning and Education, 21(2), 72-84.
What Is Executive Function? And How Does It Relate to Child Development? (N.D.) Center for the Developing Child Harvard University. https://developingchild.harvard.edu/resources/what-is-executive-function-and-how-does-it-relate-to-child-development/